However, 11 of 13 evaluableThis translocation results in the chimeric ASPSCR1TF transcription factor which drives tumorigenesis Complete surgical resection is crucial in allowing a successful outcome in these cases Here, we describe an 11monthold female infant who presented with a wellcircumscribed lesion of the tongue, with the clinical and radiologicASPSCR1TF In order to characterize the fusion gene associated with ASPS and its role in sarcomagenesis, we created a novel mouse allele designed to express ASPSCR1TF conditionally Briefly, the Rosa26LSLAT3 allele was generated by isolating the type 2 ASPSCR1TF fusion gene transcript from total RNA obtained from a human ASPS
Www Cell Com Cancer Cell Pdfextended S1535 6108 14 3
Aspscr1-tfe3
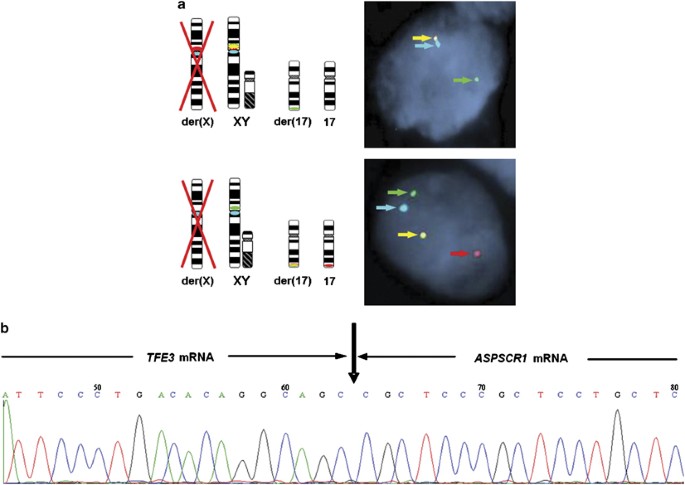
Aspscr1-tfe3- Breakpoint for translocation to form NONOTF, PSFTF and ASPSCR1TF oncogenes 2 Keywords Disease i Protooncogene Organismspecific databases DisGeNET i 7030 MalaCards i TF OpenTargets i ENSG Orphanet i , Alveolar soft tissue sarcoma RTPCR was performed to confirm the presence of an ASPSCR1TF and PRCCTF fusion transcript by using forward primers from the ASPSCR1 and PRCC sequence and a reverse primer from TF exon The image result ( Figure 6 ) showed specific ASPSCR1TF and PRCCTF products which confirmed the diagnosis of TF RCC and also identified the




New Aspscr1 Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinomas With T X 17 P11 Q25 A E H Download Scientific Diagram
Melanotic subtype generally harbors the SFPQTF fusion and rarely ARID1BTF Plasmid construction Nterminal FLAGtagged ASPSCR1TF was introduced into both the pMYsIRESGFP and pMYsIRESLuc vectors The fulllength ASPSCR1TF was cloned from a human ASPS case Artificial chimeric ASPSCR1 fusions between ASPSCR1 and TFEB, TFEC, or MITF were also generated by twostep PCR using primers encompassing both ASPSCR1 andNo fusionnegative case has ever been described Complete surgical excision, including lung metastasectomy when applicable, is the primary treatment, with limited benefit associated with chemotherapy or radiation There has been one published case of primary ASPS in the bladder
Oncogenic rearrangements of the TF transcription factor gene are found in two distinct human cancers These include ASPSCR1TF in all cases of alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) and ASPSCR1TF, PRCCTF, SFPQTF and others in a subset of paediatric and adult RCCs Here we examined the functi The difference in expression of cathepsin K between the PRCCTF and ASPSCR1TF carcinomas, together with the observed clinical differences between these subtypes of Xp11 translocation The ASPSCR1 TF fusion gene retains the DNA binding and activation domain of TF, whereas the Nterminal region of TF is replaced with ASPSCR1 sequences ASPSCR1 TF is known to upregulate the Met receptor tyrosine kinase gene and induce oncogenic phenotypes such as uncontrolled cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis
Regional lymph nodes were involved by metastasis in 24 of the 32 ASPSCR1TF cases in which nodes were resected, compared with 5 of 14 PRCCTF cases (P=002);3 ASPSCR1 TEXT A number sign (#) is used with this entry because some cases of alveolar soft part sarcoma have been found to be caused by fusion of the ASPSCR1 () and TF () genes Description Alveolar soft part sarcoma is an unusual tumor with highly characteristic histopathology and ultrastructureTether containing UBX domain for GLUT4 (TUG) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASPSCR1 gene This gene is a candidate gene for alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) It has been found that ASPSCR1 can undergo oncogenic rearrangement with transcription factor TF gene, creating an aberrant gene that is a stronger transcriptional activator than TF alone




Modeling Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Unveils Novel Mechanisms Of Metastasis Cancer Research




New Aspscr1 Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinomas With T X 17 P11 Q25 A E H Download Scientific Diagram
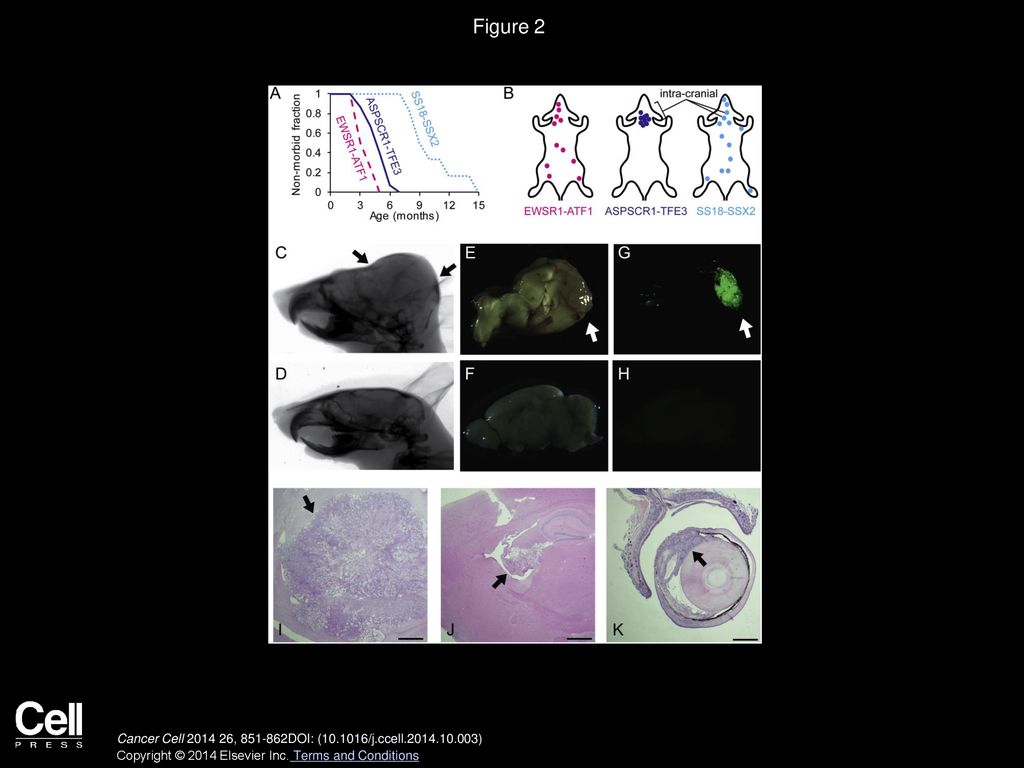
By conditionally expressing in mice the fusion gene ASPSCR1TF from human alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS), we generated a model that recapitulates the human tumor histologically and by expression profile, enabling study of the conditions supportive of tumor development Mouse tumors demonstrated angiogenic gene expression in the frank absence of hypoxia and wereDescription Homo sapiens transcription factor binding to IGHM enhancer 3 (TF), transcript variant 1, mRNA (from RefSeq NM_) RefSeq Summary (NM_) This gene encodes a basic helixloophelix domaincontaining transcription factor that binds MUtype Ebox sequences in the promoter of genes The encoded protein promotes the expression of genesA conditional expression in mice of the fusion gene ASPSCR1TF from human alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) generated a model that recapitulates the human tumor histologically and by expression profile




Aspscr1 Protein Pan Troglodytes String Interaction Network




Volume 26 Issue 6 Pages December 14 Ppt Download
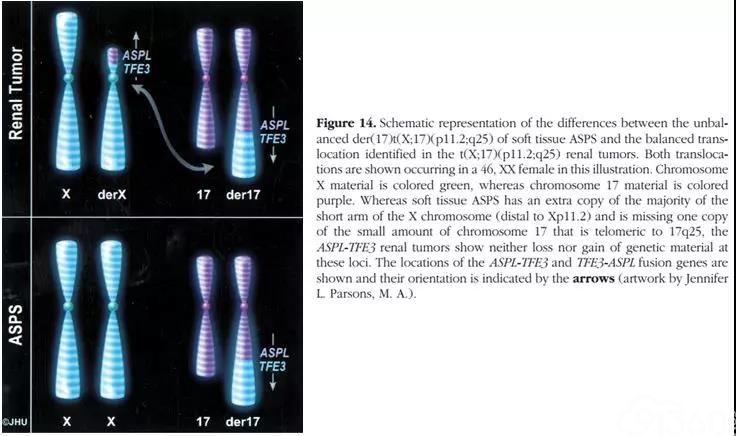
Note=A chromosomal aberration involving TF is found in patients with alveolar soft part sarcoma Translocation t(X;17)(p11;q25) with ASPSCR1 forms a ASPSCR1TF fusion protein Note=Chromosomal aberrations involving TF are found in The present model also enabled the evaluation of TFE/MITF family transcription factor function, which demonstrated that ASPSCR1TFEB possessed definitive albeit less marked oncogenic activity than that of ASPSCR1TF Collectively, our mouse model provides a tool to understand oncogenic, angiogenic, and metastatic mechanisms of ASPSAims Alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) is a rare soft tissue tumour with unique morphology and a recurrent, nonreciprocal translocation der(17)t(X;17)(p112;q25) leading to the fusion of ASPSCR1 (also known as ASPL) to the transcription factor TF Although diagnosis is straightforward in classical cases, tumours with atypical morphological features may be difficult to classify solely on




Combining Integrated Genomics And Functional Genomics To Dissect The Biology Of A Cancer Associated Aberrant Transcription Factor The Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Oncoprotein Kobos 13 The Journal Of Pathology Wiley Online Library




Molecular Genetics And Cellular Features Of Tfe3 And Tfeb Fusion Kidney Cancers Abstract Europe Pmc
Significance By conditionally expressing in mice the fusion gene ASPSCR1TF from human alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS), we generated a model that recapitulates the human tumor histologically and by expression profile, enabling study of the conditions supportive of tumor development Mouse tumors demonstrated angiogenic gene expression in the frank absence of The ASPSCR1/TF fusion replaces the Nterminal portion of TF by the fused ASPSCR1 sequences, while retaining the TF DNAbinding domain, implicating transcriptional deregulation in the pathogenesis of ASPS Ladanyi et al (01) identified major and minor splice forms of the ASPSCR1 transcript which differ by the absence or presence of a 47 These include ASPSCR1–TF in all cases of alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) and ASPSCR1–TF, PRCC‐TF, SFPQ‐TF and others in a subset of paediatric and adult RCCs Here we examined the functional properties of the ASPSCR1–TF fusion oncoprotein, defined its target promoters on a genome‐wide basis and performed a high




Signaling Schematic For Asps Tumors And Novel Therapeutic Targets A Download Scientific Diagram




Tfeb And Tfe3 Linking Lysosomes To Cellular Adaptation To Stress Abstract Europe Pmc
Alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) is an exceptionally rare nonrhabdomyosarcomatous soft tissue sarcoma (NRSTS), characterized by the translocation t(X;17) p(112;q25) This translocation results in the chimeric ASPSCR1TF transcription factor whichTF is also expressed in alveolar soft part sarcoma the hallmark of which is a chromosomal rearrangement at 17q25 and Xp112 engendering an ASPSCR1–TF fusion gene Use of this antibody is an aid in the recognition of Xp11 translocation renal cell carcinoma and alveolar soft part sarcoma within the context of an antibody panelOncogenic rearrangements of the TF transcription factor gene are found in two distinct human cancers These include ASPSCR1–TF in all cases of alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) and ASPSCR1–TF,




Molecular Genetics And Cellular Features Of Tfe3 And Tfeb Fusion Kidney Cancers Abstract Europe Pmc
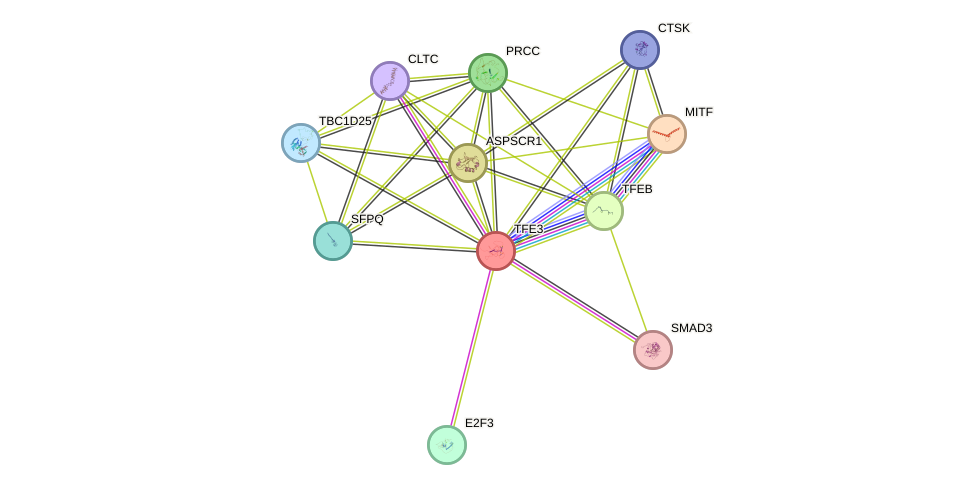



Tfe3 Protein Human String Interaction Network
A conditional expression in mice of the fusion gene ASPSCR1TF from human alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) generated a model that recapitulates the human tumor histologically and by expression profile ASPL is a cofactor of the hexameric ATPase complex, known as p97 The central area in ASPL, containing both a SHP box and a UBX domain, is The ASPSCR1TF fusion protein acts as an aberrant transcription factor resulting in activation of the MET signaling pathway believed to promote angiogenesis and cell proliferation 2 In a study performed by Tsuji et al, 22 they showed the sensitivity and specificity of TF immunohistochemistry for ASPS to be 92% and 92%, respectively Tfe3 is a critical transcription factor that regulates Pgc1alpha gene expression in myotubes;



Q Tbn And9gctj1sjz1kvtfqtqd0ibrclvzax6qnkpelftglhhewhs58musysj Usqp Cau




Rt Pcr Findings Identification Of The Aspscr1 Aspl Tfe3 Fusion Download Scientific Diagram
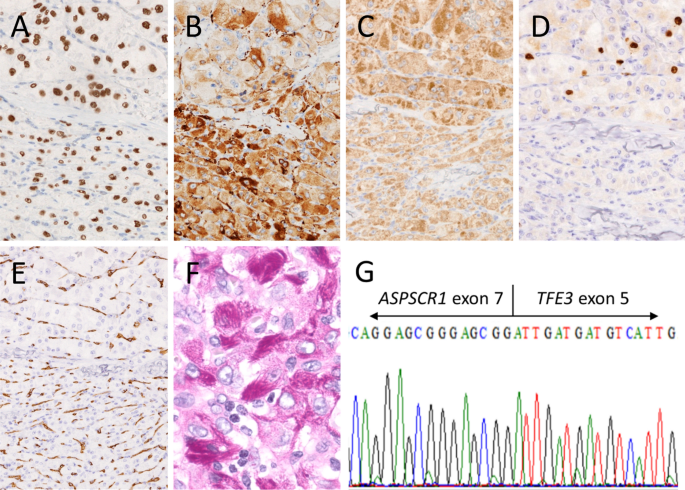
TFF Alveolar softpart sarcoma (ASPS) is a rare malignant tumor typically occurring in patients in their s to 30s within the muscle and deep tissues of the extremities ASPS is slow growing and refractory to chemotherapy with a propensity to metastasize Prolonged survival is possible even with metastasis, although the longterm diseaserelated mortality rate is highOur objective was to identify the direct targets of ASPSCR1TF and how these targets confer resistance to doxorubicin The human cell lines ASPS1 and FUUR1, as well as mouse tumors driven by expression of ASPSCR1TF were subjected to nuclear fractionation and chromatin immunoprecipitation using antibodies against ASPSCR1 and RNAPol2 Based on morphologic features (nested pattern) and the above IHC results including strong TF expression, ASPS was a strong consideration Although fluorescence in situ hybridization results were positive for TF gene rearrangement, the specific TF/ASPSCR1 rearrangement (X17




Volume 26 Issue 6 Pages December 14 Ppt Download



Www Cell Com Cancer Cell Pdfextended S1535 6108 14 3
Note the t(X;17)(p11;q25) in primary renal ASPSCR1TF tumours is balanced in all known cases Genes involved and Proteins Note Retention of heterozygocity in the tumours of female patients (ie a normal maternal X and a normal paternal X are present, in addition to the Xp11pter involved in the translocation) has been noted in all (n=7 The ASPSCR1/TF fusion replaces the Nterminal portion of TF by the fused ASPSCR1 sequences, while retaining the TF DNAbinding domain, implicating transcriptional deregulation in the pathogenesis of ASPS Heimann et al (01) identified the ASPSCR1 gene, which they called RCC17, partnered with TF in two 5yearold Belgian girls of Cases with ASPSCR1TF, SFPQTF, PRCCTF, and NONOTF gene fusion showed a wide variability in morphologic features, including invasive tubulopapillary pattern simulating collecting duct carcinoma, extensive calcification and ossification, and overlapping and high columnar cells with nuclear grooves mimicking tall cell variant of




Tfe3 Syntezza Bioscience




Neat1 Tfe3 And Kat6a Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinomas New Members Of Mit Family Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma Modern Pathology X Mol
ASPSCR1TF alveolar soft part sarcoma Pubmed 17 ASPSCR1TF ASPSCR1TF Adenocarcinoma, Alveolar soft part sarcoma, renal cell carcinoma PubmedIn addition to wildtype TF, ASPSCR1TF fusion transcripts (three type 1 and two type 2 transcripts) were detected in all cases CONCLUSIONS Molecular confirmation of ASPSCR1TF gene fusion is applicable to routinely processed archival and diagnostic tumour samples and aids in the differential diagnosis of ASPS PMID Alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) is a rare malignancy that, since its initial description, remains a neoplasm of uncertain histogenesis The diseasedefining molecular event characterizing the diagnosis of ASPS is the ASPSCR1TF fusion gene Following identification of an index case of ASPS with




Rt Pcr Findings Identification Of The Aspscr1 Aspl Tfe3 Fusion Download Scientific Diagram




Comparison Of Aspscr1 Tfe3 And Prcc Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinomas Download Table
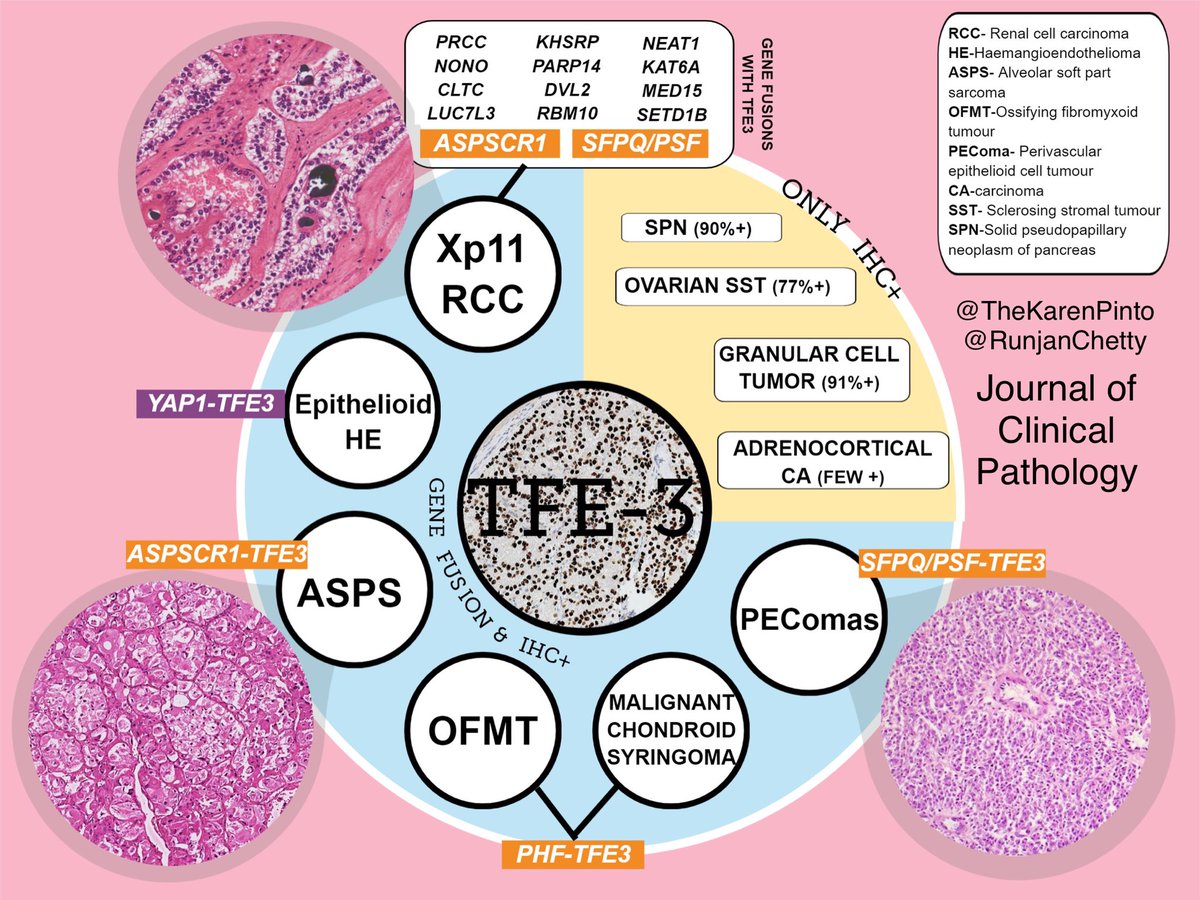
The hallmark of ASPS is a chromosomal rearrangement at 17q25 and Xp112 engendering an ASPSCR1TF fusion gene responsible for an aberrant transcription factor presumably enabling pathogenesisThis aberrant chimeric transcription factor retains the Nterminal DNA binding domain encoded by TF while the ASPSCR1 encoded portion probablyTF is also rearranged with ASPSCR1 and other genes in rare forms of renal cell carcinoma, which are most common in children 42 Interestingly, the TFASPSCR1 translocations in the renal cell carcinomas tend to be balanced, whereas the translocation is unbalanced in alveolar soft part sarcoma (Fig 1812A)A fusion partner was identified in 53/60 (%) cases, including 18 SFPQ (PSF), 16 PRCC, 12 ASPSCR1 (ASPL), 6 NONO, and 1 DVL2 We provide the first morphologic description of the NONOTF RCC, which frequently demonstrates subnuclear vacuoles leading to distinctive suprabasal nuclear palisading



Q Tbn And9gcschgym8b8jialvutakgwnd0140i600izowuxoxj2yirhrgtrez Usqp Cau



Kidney Renal Cell Carcinoma With T X 17 P11 Q25 Aspscr1 Tfe3
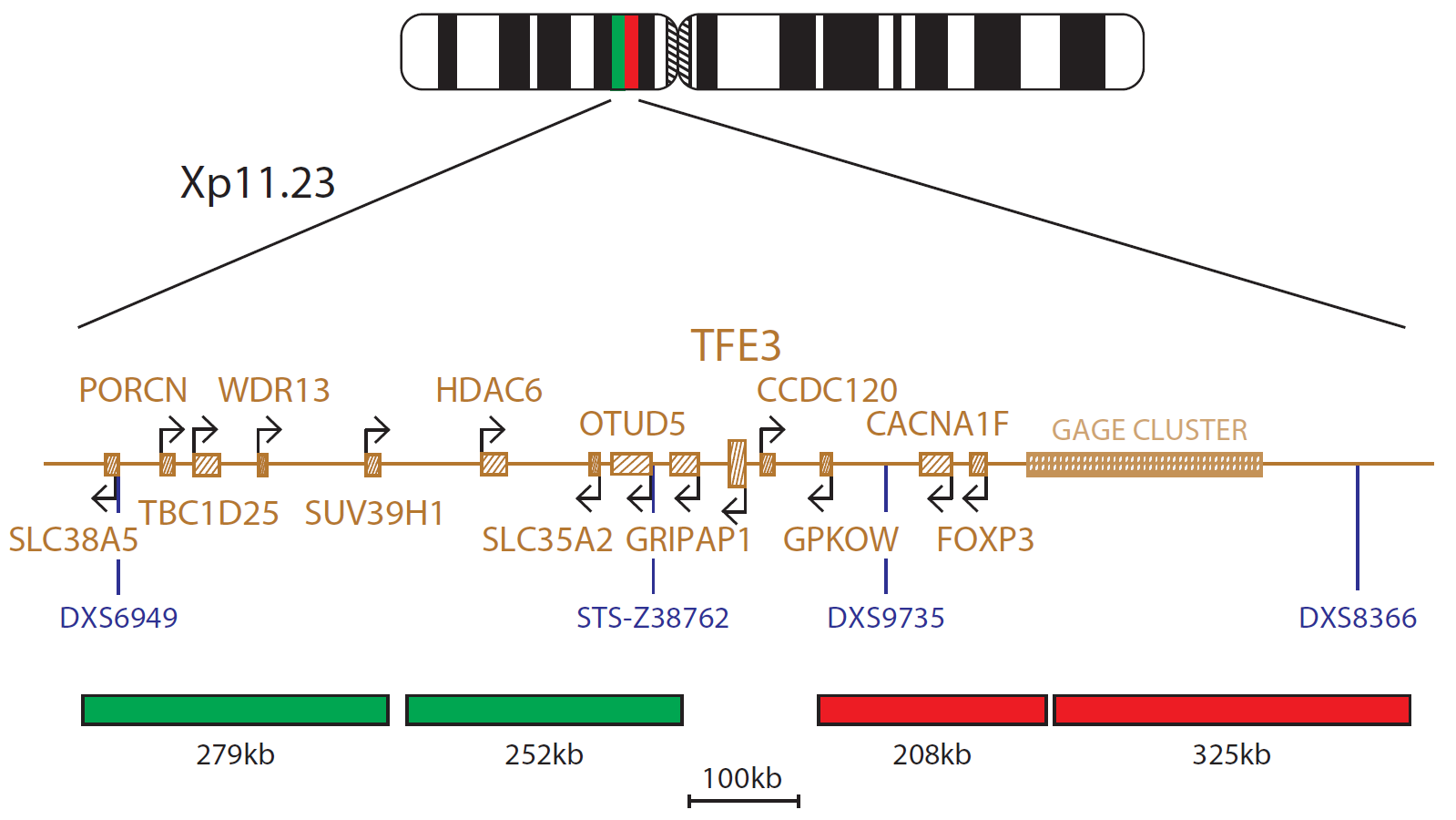
The reciprocal 5' TF 3' ASPSCR1 is most often absent ASPSCR1 is fused in frame to TF exon 3 or 4 Abnormal Protein NH2 term ASPSCR1, fused to the C term of TF Oncogenesis might combine the effect of a fusion protein to that of gene(s) dosage Entity primary renal ASPSCR1TF tumour Disease YAP1TFfused hemangioendothelioma is an extremely rare malignant vascular tumor, with only a few dozen cases reported, most of which were single case reports or larger case series that combineSoft Tissue Sarcoma Diagnostic Kit The ASPSCR1TF Fusion/Translocation FISH Probe Kit is designed to detect rearrangements involving the human ASPSCR1 and TF genes located on chromosome bands 17q253 and Xp1123, respectivelyFusion of ASPSCR1 – also known as TUG, ASPL, ASPS, RCC17, UBXD9, UBXN9 or ASPCR1 – with the TF gene – also known as TFEA,
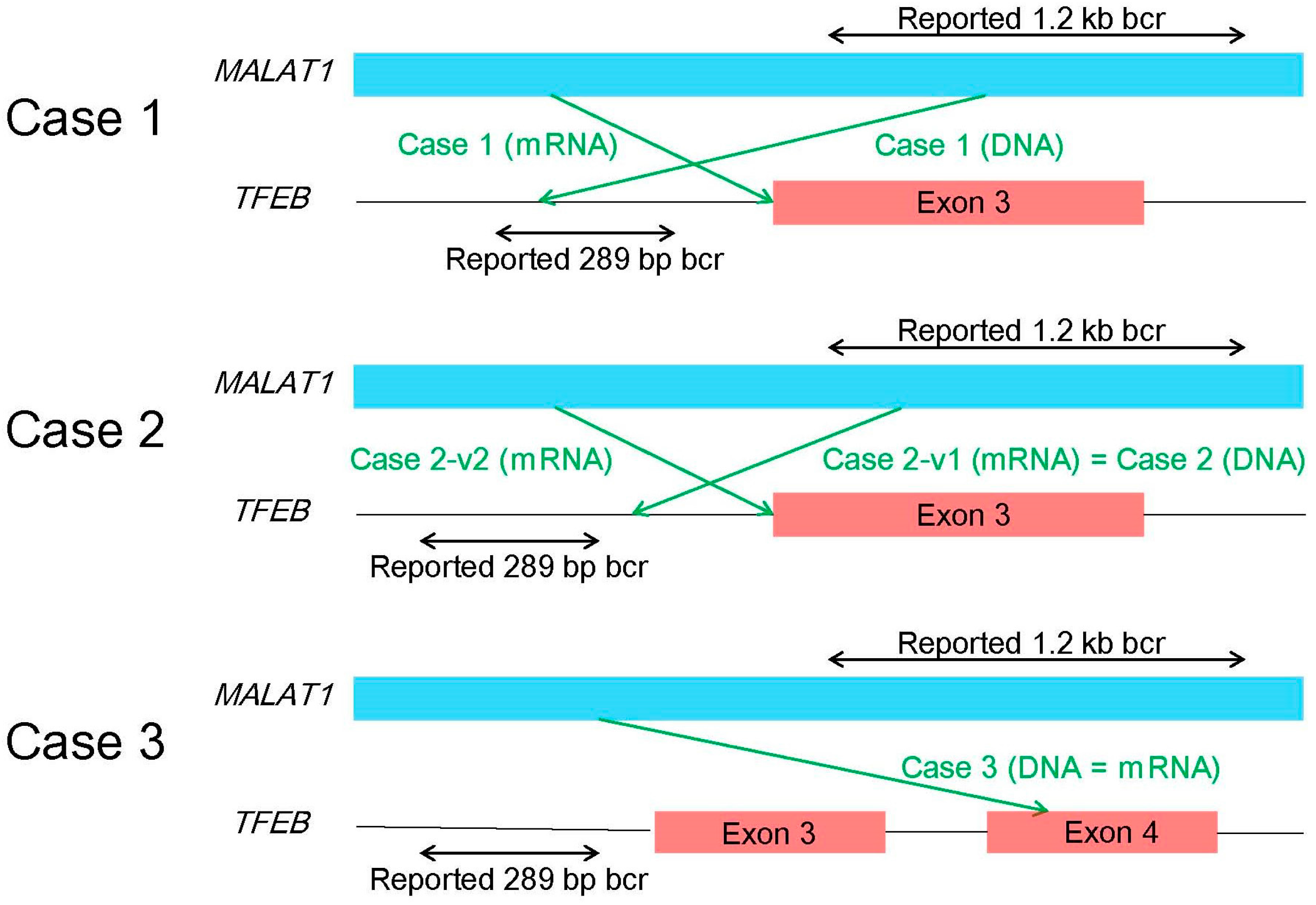



Cancers Free Full Text Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma An Update On Clinicopathological And Molecular Features Html




Alveolar Soft Part Sarcomas Molecular Pathogenesis And Implications For Novel Targeted Therapies
Abstract B54 Enhancer reprogramming by ASPSCR1TF in alveolar soft part sarcoma Miwa Tanaka and Takuro Nakamura Miwa Tanaka The Cancer Inst, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research, Tokyo, Japan Find this author on Google Scholar Find this author on PubMed Search for this author on this site TF break apart probes in FISH analysis are most effective at detection of the fusion due to multiple partners of the gene ;Disease ASPSCR1/TF renal cell carcinomas harbor the same gene fusion as alveolar soft part sarcoma, but belong to the family of Xp11 translocation RCCXp11 translocation renal cell carcinoma (RCCs) harbor gene fusions involving TF transcription factor The The t(6;11) RCCs harbor a specific MALAT1 (Alpha) TFEB gene fusion TFEB and TF belong to the same MiT subfamily



Tfe3 Transcription Factor



Kidney Renal Cell Carcinoma With T X 17 P11 Q25 Aspscr1 Tfe3
Aims Alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) is a rare soft tissue tumour with unique morphology and a recurrent, non‐reciprocal translocation der(17)t(X;17)(p112;q25) leading to the fusion of ASPSCR1 (also known as ASPL) to the transcription factor TF Although diagnosis is straightforward in classical cases, tumours with atypical morphological features may be difficult Even our data showed that NONOTF RCC patients had a longer survival than ASPSCR1TF RCC and PRCCTF RCC in a short time followup study However, there was a case at the pT1aM0N0 stageThe most common partner genes in MiT family translocation associated renal cell carcinoma are PRCC and ASPSCR1 (ASPL) (Am J Surg Pathol 16;);



Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Translocation Fish Probe Kit 10 Tests Diagnostic Technology



Aspscr1 Wikipedia
A total of five TF gene fusions (PRCCTF, ASPSCR1TF, SFPQTF, NONOTF, and CLTCTF) and one TFEB gene fusion (MALAT1TFEB) have been identified in RCC tumours and characterized at the mRNA transcript level A multitude of molecular pathways welldescribed in carcinogenesis are regulated in part by TF or TFEB proteins, including ASPSCR1TF is the driving oncogenic feature of this tumor type;PMID 6695 Alveolar soft part sarcoma a bimarker diagnostic strategy using TF immunoassay and ASPLTF fusion transcripts in paraffinembedded tumor tissues Pang LJ, Chang B, Zou H, Qi Y, Jiang JF, Li HA, Hu WH, Chen YZ, Liu CX, Zhang WJ, Li F Diagn Mol Pathol 08 Dec;17 (4) doi /PDM0b013ed68d7




Comparison Of Aspscr1 Tfe3 And Prcc Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinomas Download Table



Q Tbn And9gcqmp7zvhkffac6grr6l046qwboj2qozedb5urd Hrgdw H69zzp Usqp Cau




Comparison Of Aspscr1 Tfe3 And Prcc Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinomas Download Table




Comparison Of Aspscr1 Tfe3 And Prcc Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinomas Download Table




Genetic Diversity In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma A Subset Contain Variant Fusion Genes Highlighting Broader Molecular Kinship With Other Mit Family Tumors Dickson Genes Chromosomes And Cancer Wiley Online Library




Incidence Clinicopathological Features And Fusion Transcript Landscape Of Translocation Renal Cell Carcinomas Classe 17 Histopathology Wiley Online Library



Www Cell Com Cancer Cell Pdfextended S1535 6108 14 3
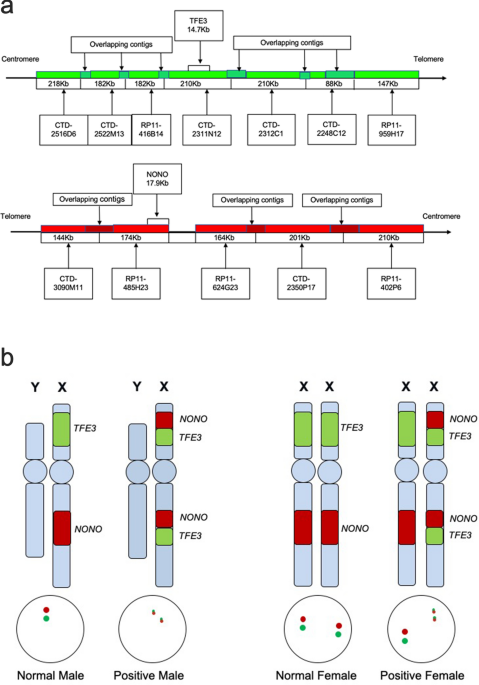



The Suitability Of Nono Tfe3 Dual Fusion Fish Assay As A Diagnostic Tool For Nono Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinoma Scientific Reports




Comparison Of Aspscr1 Tfe3 And Prcc Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinomas Download Table



Lesterthompsonmd Com Pdf Hnpj 13 03 Oral alveolar soft part sarcoma Pdf




Alveolar Soft Part Sarcomas Molecular Pathogenesis And Implications For Novel Targeted Therapies



Cytocell Tfe3 Breakapart Fish Probe Ogt



Primary Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Of Cheek Report Of A Case And Review Of The Literature Springerlink



Tfe3 Mrq 37 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody




Technique For Differentiating Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma From Other Tumors In Paraffin Embedded Tissue Comparison Of Immunohistochemistry For Tfe3 And Cd147 And Of Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction For Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Transcript



Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Translocation Fish Probe Kit 10 Tests Diagnostic Technology




Alveolar Soft Part Sarcomas Molecular Pathogenesis And Implications For Novel Targeted Therapies




Activity And Safety Of Crizotinib In Patients With Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma With Rearrangement Of Tfe3 European Organization For Research And Treatment Of Cancer Eortc Phase Ii Trial Create Annals



2




Alveolar Soft Part Sarcomas Molecular Pathogenesis And Implications For Novel Targeted Therapies




Marc Ladanyi Yes Most Alveolar Soft Part Sarcomas Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Would Be Considered To Fall In The Simple Reciprocal Translocation Group Blast From The Past Some Of Our Work




Table 1 From Mit Family Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma Semantic Scholar



Http Protilatky Biopticka Cz Home Download 366
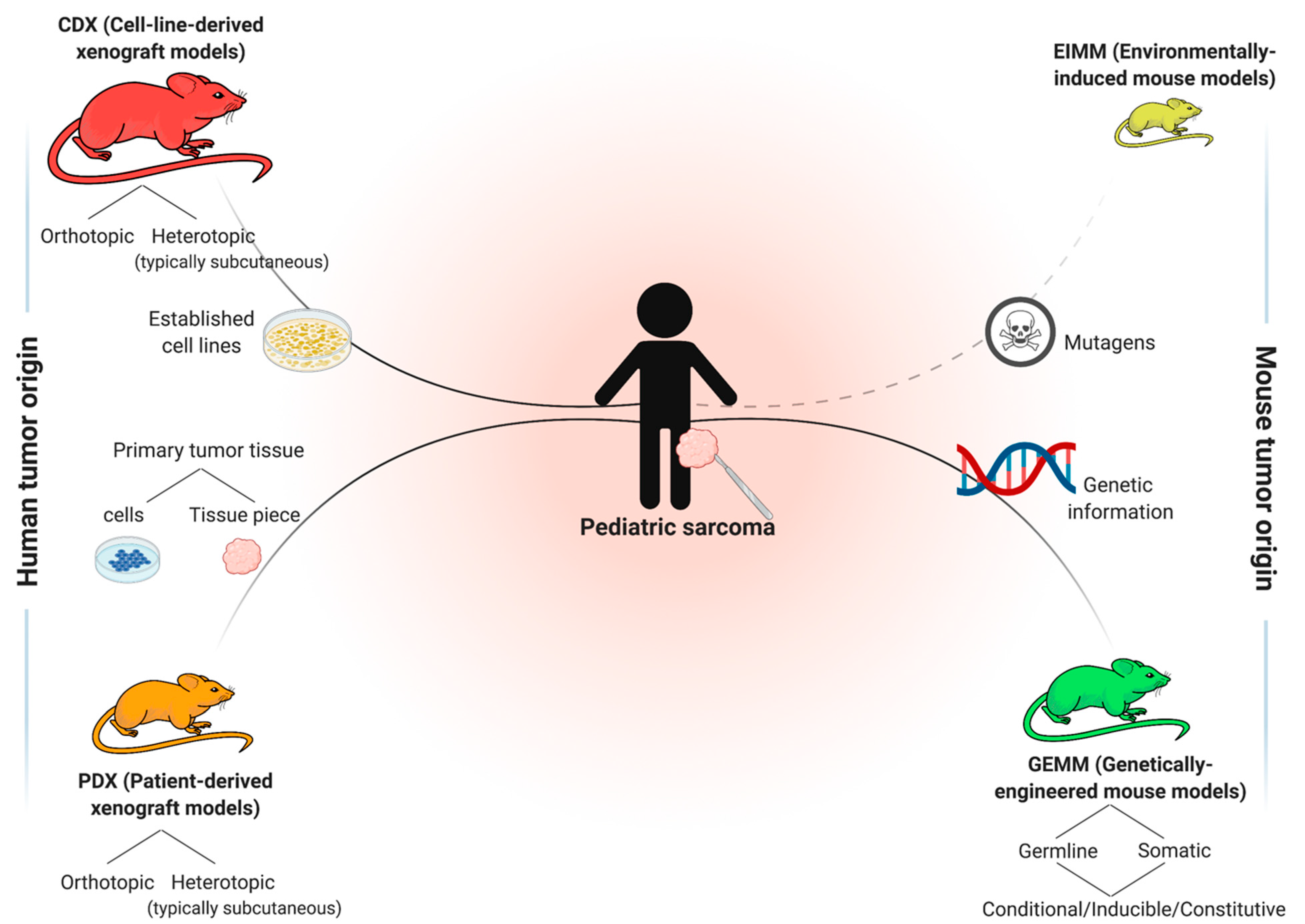



Jcm Free Full Text Preclinical In Vivo Modeling Of Pediatric Sarcoma Promises And Limitations Html




New Aspscr1 Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinomas With T X 17 P11 Q25 A E H Download Scientific Diagram



Clincancerres crjournals Org Content Clincanres Early 14 07 10 1078 0432 Ccr 13 3036 Full Text Pdf



Volume 26 Issue 6 Pages December 14 Ppt Download




Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Of The Bladder With Aspscr1 Tfe3 Gene Fusion As A Secondary Malignancy Sciencedirect
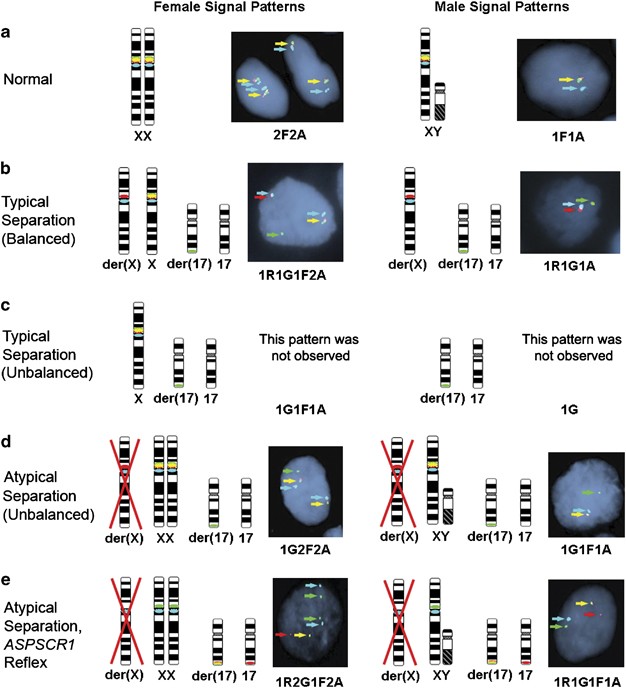



Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis For Tfe3 Rearrangement In Xp11 2 Renal Cell Carcinoma And Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Validation And Clinical Experience With 75 Cases Modern Pathology




Tfe3 Antibody Ihc672 Genomeme




Modeling Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Unveils Novel Mechanisms Of Metastasis Cancer Research




Technique For Differentiating Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma From Other Tumors In Paraffin Embedded Tissue Comparison Of Immunohistochemistry For Tfe3 And Cd147 And Of Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction For Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Transcript



Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis For Tfe3 Rearrangement In Xp11 2 Renal Cell Carcinoma And Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Validation And Clinical Experience With 75 Cases Modern Pathology




Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Of The Bladder With Aspscr1 Tfe3 Gene Fusion As A Secondary Malignancy Sciencedirect




The T X 17 P11 25 Translocation A The Aspscr 1 Gene Is Located At Download Scientific Diagram



Q Tbn And9gcsufh Vvzx9 H0rrk4ov0p7fskteghigihfeaslu2stacomokjs Usqp Cau




Angiogenesis Promoting Gene Patterns In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Clinical Cancer Research



Www Cell Com Cancer Cell Pdfextended S1535 6108 14 3



2




Modeling Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Unveils Novel Mechanisms Of Metastasis Cancer Research




Genomics Morphoproteomics And Treatment Patterns Of Patients With Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma And Response To Multiple Experimental Therapies Molecular Cancer Therapeutics



Kidney Renal Cell Carcinoma With T X 17 P11 Q25 Aspscr1 Tfe3



Tfe3 Transcription Factor




Integrative Clinical And Molecular Characterization Of Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma Biorxiv
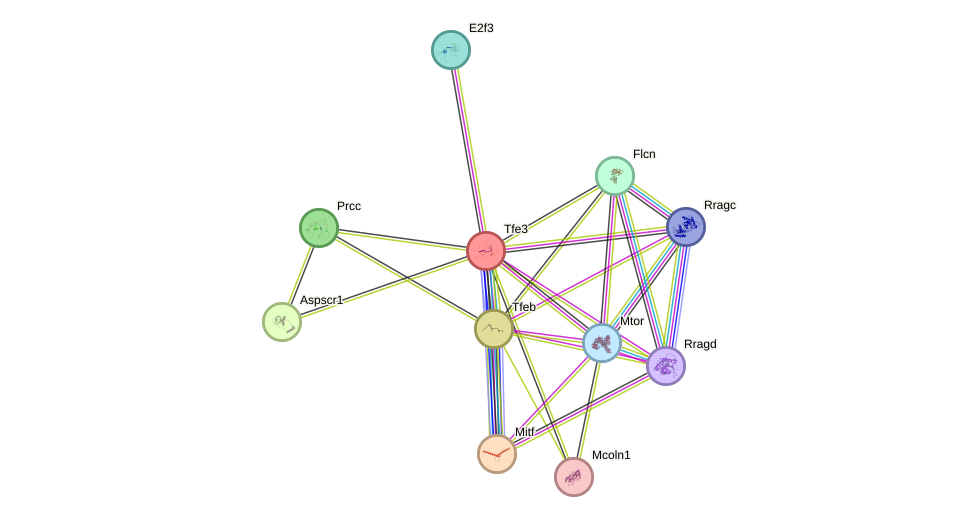



Tfe3 Protein Mouse String Interaction Network




Molecular Landscape In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Implications For Molecular Targeted Therapy Sciencedirect




Molecular Landscape In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Implications For Molecular Targeted Therapy Sciencedirect



Http Www Ijcep Com Files Ijcep Pdf




Volume 26 Issue 6 Pages December 14 Ppt Download



乱花渐欲迷人眼 Aspscr1 Tfe3融合在不同肿瘤中阳性类型表现不同



Largest Trial Ever Performed In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Results Published 21 Eortc Eortc



Karen Pinto Dnb Frcpath All You Need To Know About Tfe3 Gene Sometimes Called Tfea Image 2 Tumours With Tfe3 Gene Fusions Ihc As Well As Those Which



Comparison Of Aspscr1 Tfe3 And Prcc Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinomas Download Table
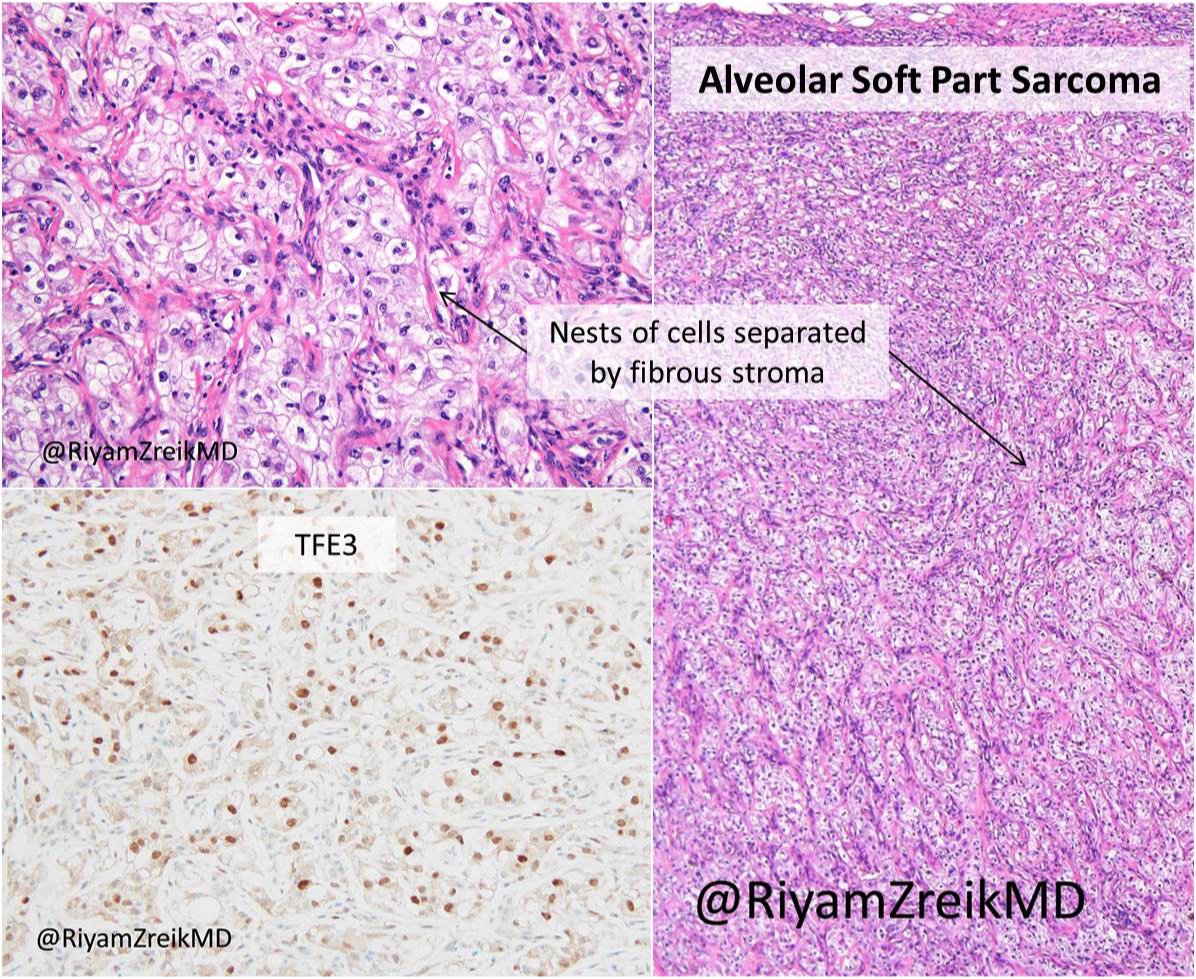



Texas Soc Of Pathol Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Is A Rare Tumor Of Deep Soft Tissue Characterized By Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Aspscr1 Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Critical Region 1 Bstpath




Genetically Confirmed Aspscr1 Tfe3 Renal Cell Carcinomas Download Table




Technique For Differentiating Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma From Other Tumors In Paraffin Embedded Tissue Comparison Of Immunohistochemistry For Tfe3 And Cd147 And Of Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction For Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Transcript




Aspscr1 Gene Genecards Aspc1 Protein Aspc1 Antibody




Combining Integrated Genomics And Functional Genomics To Dissect The Biology Of A Cancer Associated Aberrant Transcription Factor The Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Oncoprotein Kobos 13 The Journal Of Pathology Wiley Online Library




Combining Integrated Genomics And Functional Genomics To Dissect The Biology Of A Cancer Associated Aberrant Transcription Factor The Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Oncoprotein Kobos 13 The Journal Of Pathology Wiley Online Library




Combining Integrated Genomics And Functional Genomics To Dissect The Biology Of A Cancer Associated Aberrant Transcription Factor The Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Oncoprotein Abstract Europe Pmc
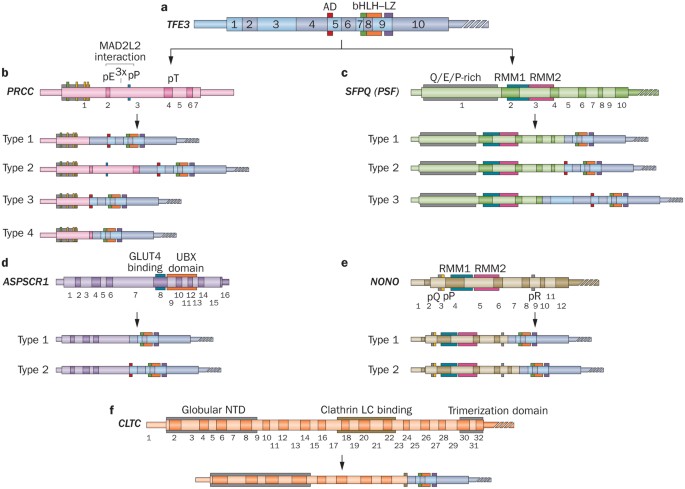



Molecular Genetics And Cellular Features Of Tfe3 And Tfeb Fusion Kidney Cancers Nature Reviews Urology
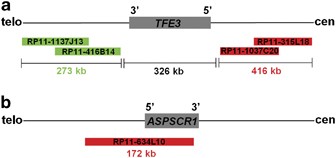



Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis For Tfe3 Rearrangement In Xp11 2 Renal Cell Carcinoma And Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Validation And Clinical Experience With 75 Cases Modern Pathology




X 17 P11 Q25 Aspscr1 Tfe3 Translocation Renal Cell Carcinomas Download Scientific Diagram



Www Cell Com Cancer Cell Pdfextended S1535 6108 14 3



Tfe3 Transcription Factor




Aspscr1 Tfe3 Fusion Translocation Fish Probe Kit Cytotest




Abstract B The Molecular Function Of Aspscr1 Tfe3 In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Clinical Cancer Research
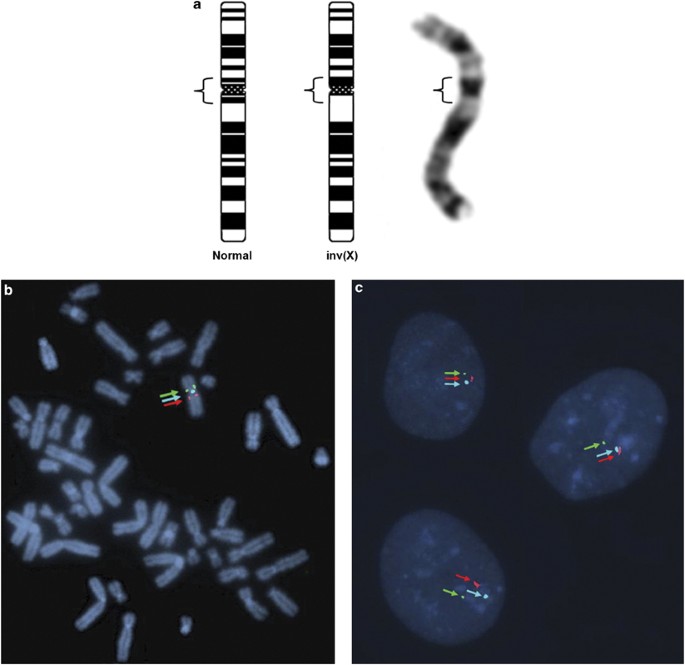



Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis For Tfe3 Rearrangement In Xp11 2 Renal Cell Carcinoma And Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Validation And Clinical Experience With 75 Cases Modern Pathology




Rt Pcr Findings Identification Of The Aspscr1 Aspl Tfe3 Fusion Download Scientific Diagram
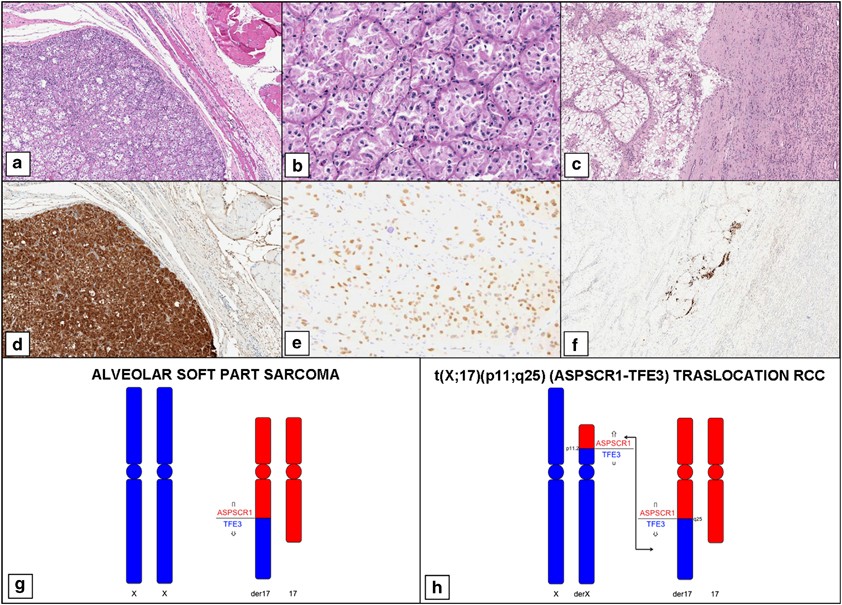



Differential Expression Of Cathepsin K In Neoplasms Harboring Tfe3 Gene Fusions Modern Pathology
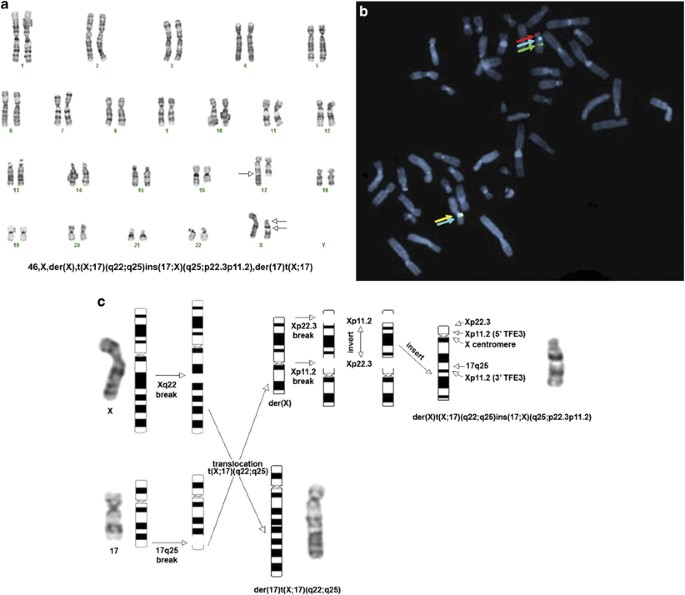



Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis For Tfe3 Rearrangement In Xp11 2 Renal Cell Carcinoma And Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Validation And Clinical Experience With 75 Cases Modern Pathology




Recombinant Anti Tfe3 Antibody Epr Ab Abcam



Www Cell Com Cancer Cell Pdfextended S1535 6108 14 3
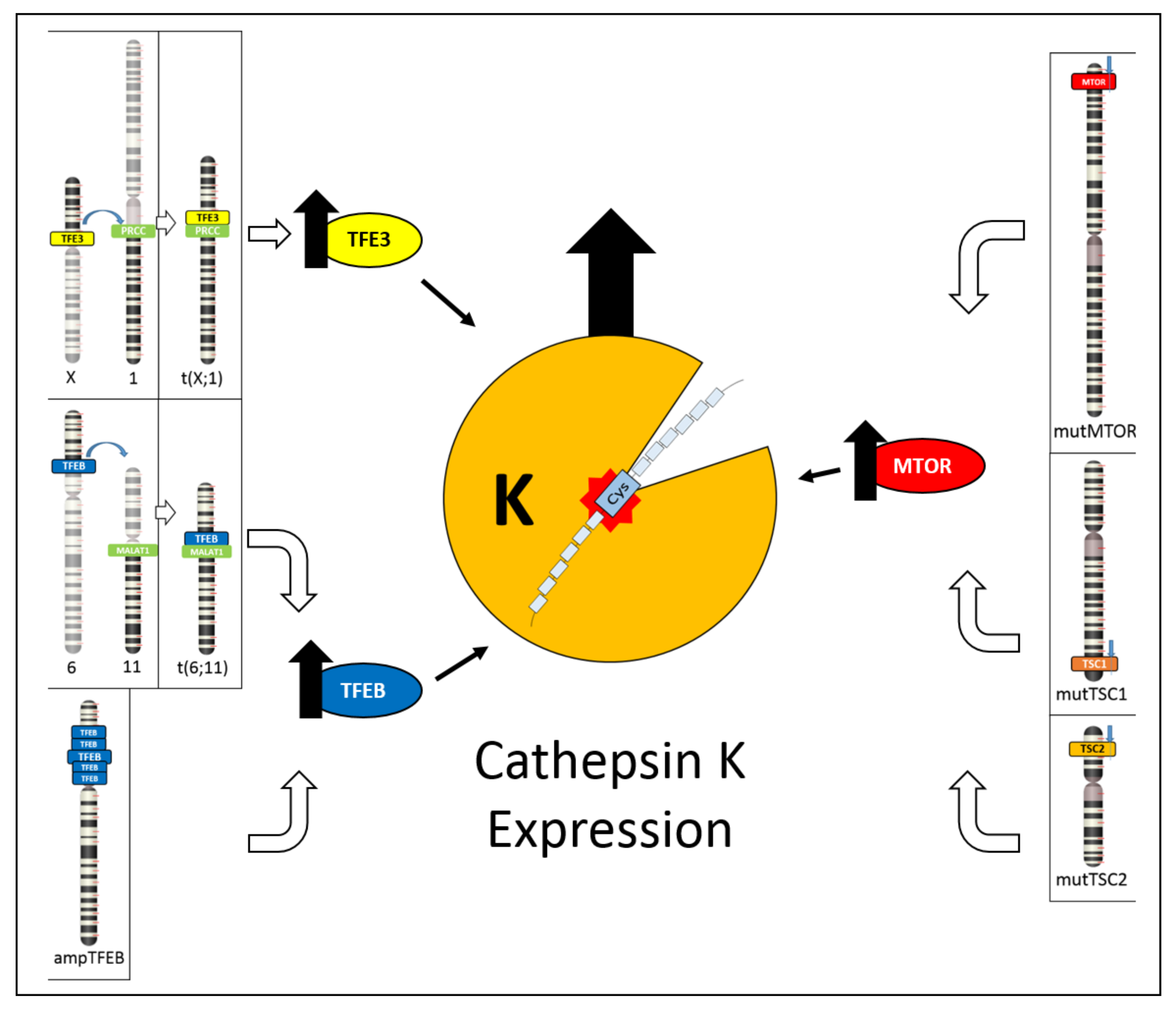



Cancers Free Full Text Cathepsin K A Novel Diagnostic And Predictive Biomarker For Renal Tumors Html




The Fusion Oncogene Aspscr1 Tfe3 Directs Epigenetic Induced Autophagy In Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Barrott 19 The Faseb Journal Wiley Online Library



Aspscr1 Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Critical Region 1
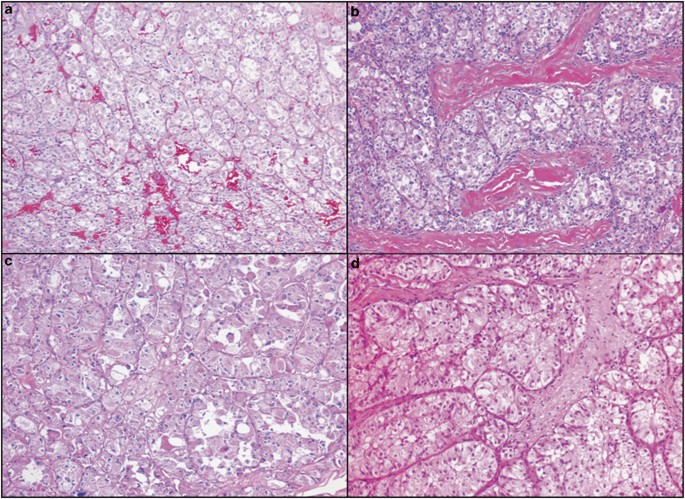



Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis For Tfe3 Rearrangement In Xp11 2 Renal Cell Carcinoma And Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Validation And Clinical Experience With 75 Cases Modern Pathology
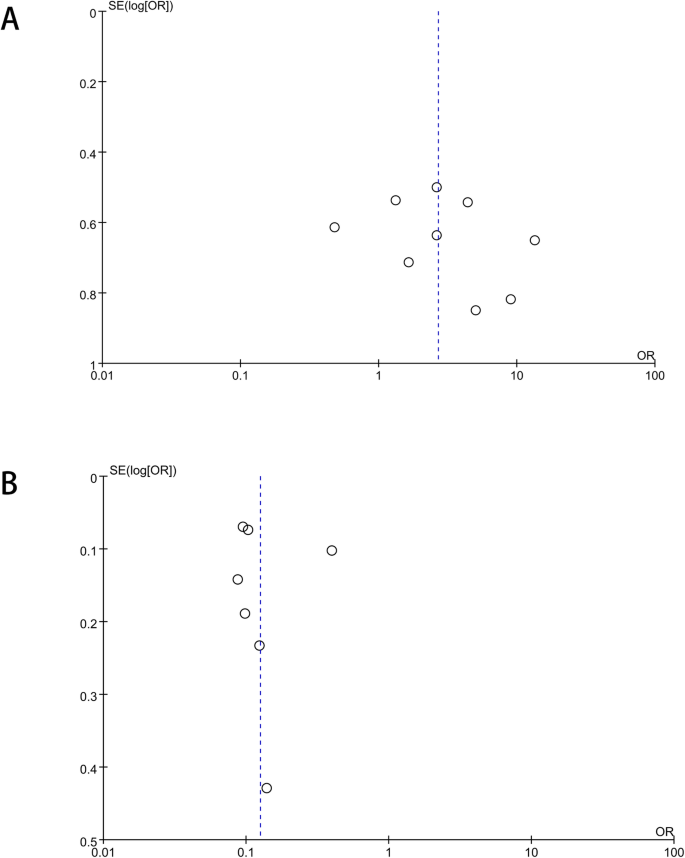



Gender Difference Analysis Of Xp11 2 Translocation Renal Cell Carcinomas S Attack Rate A Meta Analysis And Systematic Review Bmc Urology Full Text



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿